Industrial burners are indispensable in many manufacturing and processing operations, from power generation to chemical heating and material drying. Since burners are often categorized by fuel type, how do you know which fuel for burners is right for your application?
Choosing the right fuel for burners requires careful consideration of fuel efficiency, costs, emissions, and safety. You’re in the right place to find out. Career Burner will explore the most common fuels used in industrial burners to help you make the best decision for your needs!
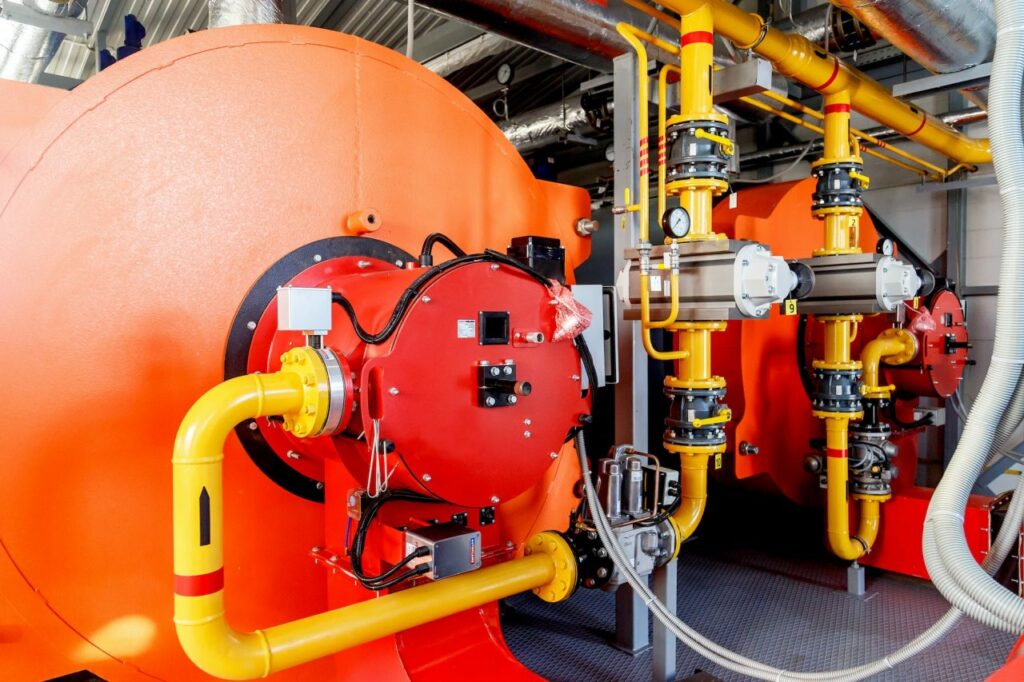
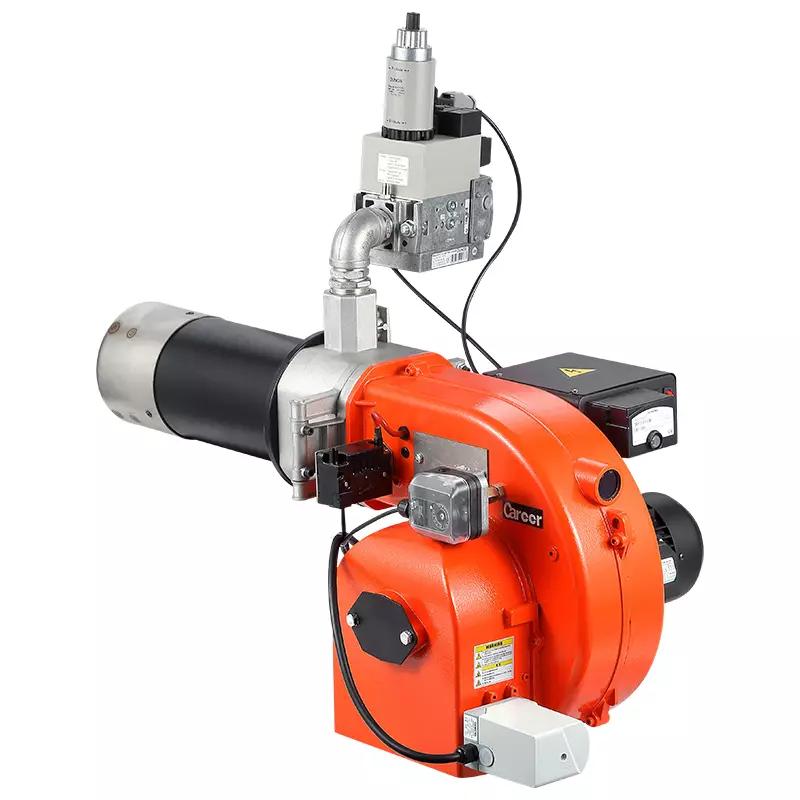
Product shown: GX60-2 Gas Fired Steam Boiler Burner
Common Types of Fuels for Burners
Industrial burners utilize various fuel sources, which can be broadly categorized into gaseous, liquid, and, less commonly, solid fuels.
- Gaseous Fuels
Gaseous fuels are highly favored for their clean combustion, ease of handling, and reliable supply, often resulting in lower maintenance costs for the equipment.
- Natural Gas
This is arguably the most common and popular fuel for burners globally. It is predominantly methane and burns cleaner than many other fossil fuels, offering high efficiency and minimal particulate matter emissions.
It is an excellent choice for applications requiring precise temperature control and clean operation. For example, our industrial natural gas burners are specifically engineered to maximize the benefits of this versatile fuel.

- Propane (Liquefied Petroleum Gas – LPG)
Propane is often used in areas where natural gas infrastructure is unavailable or as a backup fuel. It’s stored as a liquid under pressure and vaporizes before combustion. While slightly more expensive than natural gas, it offers high energy density and clean burning.
- Other Gaseous Fuels
Emerging fuels like biogas and hydrogen are gaining interest for their environmental benefits. Biogas, derived from organic waste, offers a renewable alternative, while hydrogen promises zero carbon emissions at the point of use. Though less common, these gaseous options represent the future direction for sustainable burner technologies.
- Liquid Fuels
Liquid fuels offer high energy density, making them suitable for applications requiring substantial heat output or in locations where pipeline gas is not practical.
- Light Fuel Oil (e.g., Diesel/Kerosene)
These oils are relatively low in viscosity and sulfur, leading to cleaner combustion than heavy oils. They are often used in smaller industrial burners or as a backup fuel.
- Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO/Residual Oil)
HFO is a byproduct of the refining process, making it generally cheaper than light oils. However, it requires preheating to reduce viscosity for proper atomization and combustion, and it often contains higher levels of sulfur and contaminants, necessitating more complex emission control systems and burner maintenance.
- Waste Oil
This includes used hydraulic oil, cooking oil, and other petroleum-based products. Waste oil burners provide a cost-effective and environmentally responsible way to convert such waste into useful energy.
However, waste oil requires specialized filtration and pretreatment to remove contaminants and water, as well as specific burner systems designed to handle its variable consistency and high viscosity.
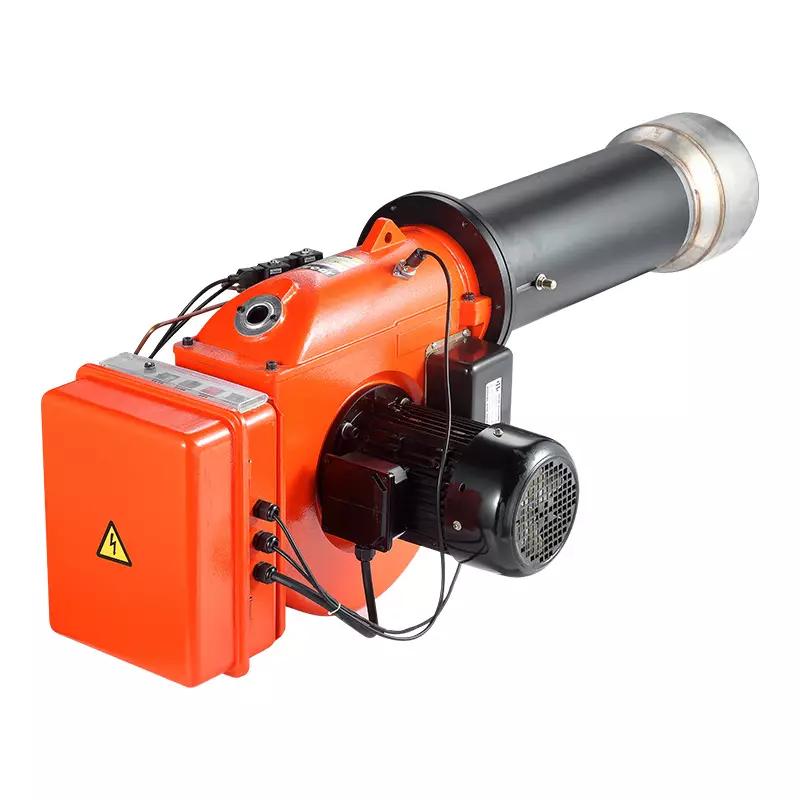
Product shown: FX20 Automatic Waste Oil Burner
- Biofuels (e.g., Biodiesel)
These are derived from renewable sources like vegetable oils or animal fats. Biofuels can significantly reduce the net carbon footprint of an operation. They can often be blended with or even replace traditional petroleum-based fuel for burners with minimal modifications. However, availability and cost may vary by region.
- Solid Fuels
While less common in modern industrial burners, solid fuels like coal or biomass pellets are still relevant in certain sectors. These fuels require specific burner designs and handling systems due to their physical properties but remain an option, especially in regions where gaseous or liquid fuels are scarce or costly.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Fuel for Burners
To choose the ideal fuel for burners, you can start your considerations according to the following:
- Energy Efficiency
Efficiency determines how much heat energy is extracted from the fuel. Natural gas and propane often deliver higher energy efficiency, making them preferred options for optimizing fuel consumption.
- Emissions and Environmental Impact
Stricter environmental regulations are pushing industries to reduce emissions. Gaseous fuels tend to emit less carbon dioxide and particulates compared to heavy oils, while biofuels and hydrogen offer even cleaner alternatives. If you must use heavier oils, you will need to budget for advanced flue gas treatment and monitoring.
- Availability and Supply Stability
You should choose fuel that can be reliably sourced and delivered to your location, as this is essential for uninterrupted operations. While natural gas is widely available in many regions, industries in remote areas may rely more on propane, fuel oils, or even dual fuel burners for boilers to ensure flexibility.
- Safety and Handling
Each fuel type carries different handling and storage requirements. Liquid fuels require tanks and pumping systems, while gaseous fuels require pressure regulation and robust leak detection. Evaluate whether your workspace can accommodate the necessary storage conditions to ensure proper handling and optimal safety.
- Cost Implications
This is not just the price per unit of energy but the total cost, including storage, handling, pretreatment (like preheating heavy oil), burner maintenance, and compliance with emission standards. A cheaper fuel may lead to higher long-term operational costs due to maintenance and environmental fines.
At Career Burner, we are committed to providing tailored solutions. We offer a comprehensive range of industrial gas burners and industrial oil burners—including ultra-low NOx gas burners—engineered for optimal performance, efficiency, and environmental compliance, no matter your primary fuel source.
Conclusion
The choice of fuel for burners has a direct impact on efficiency, emissions, safety, and overall costs. It is essential to carefully analyze whether you prioritize the clean burn and convenience of gas fuel or the high energy density of fuel oil.
At Career Burner, we take pride in helping industries find the most suitable burner solutions. Our expertise spans textile dyeing and finishing, waste incineration, industrial boilers, pretreatment drying, and more.
Learn more about how we can support your needs—contact us today!